Business Use Cases Can Help Users Understand the Value of Augmented Analytics!

Gartner predicts that, ‘Through 2025, 80% of organizations seeking to scale digital business will fail because they do not take a modern approach to data and analytics governance.’ In order to succeed in market competition and increased performance, every business must consider the addition of self-serve augmented analytics for business users. Giving team members these tools assures that data is integrated and used to make fact-based decisions with measurable results.
‘While every business can and should develop a set of business use cases that will apply to its own unique industry, function and/or issues, your enterprise can use these sample use cases to illustrate the usefulness of augmented analytics.’
When a business undertakes an initiative to transition business users to Citizen Data Scientists, it often struggles to show the value and benefit of these tools to its team members. Whether you are implementing a new self-serve augmented analytics project, or expanding an initiative, it is important to get your business users on board. This goal can be achieved by showing team members how to apply analytical techniques and algorithms to day-to-day issues, problems, and projects.
Business Use Cases can be helpful in this effort, as they provide a clear picture of a story of a problem that is familiar to business users and a clear picture of how the augmented analytics solution can help the user to understand the root cause of a problem, identity trends, spot opportunities, etc.
We invite you to explore these Business Use Case examples contained within each of these links and to share these with your users to help them understand how augmented analytics tools and analytical techniques can be used to understand challenges and opportunities and to strategize and share data.
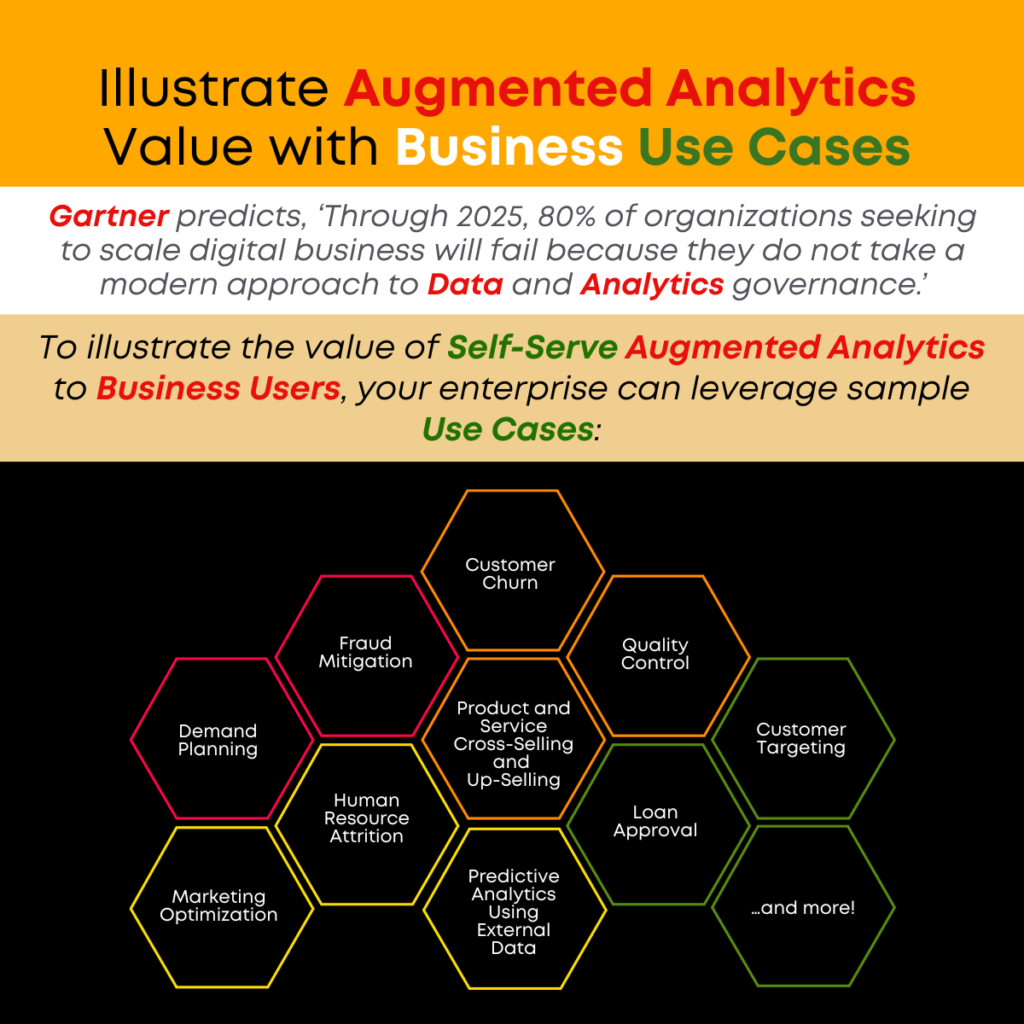
Customer Churn
The cost of acquiring and interacting with customers is one a business must fund and, every time the business loses a customer (customer churn), it must spend more money to replace that customer.
Fraud Mitigation
Businesses must work to mitigate fraud to improve business results and develop and sustain fraud detection processes to enable operations monitoring.
Quality Control
Businesses that fail to control quality will lose customers and market share and, in some cases, expose the organization to legal risk and liability.
Demand Planning
Businesses cannot afford to use guesswork in the planning process. There are many factors that influence business success and a business must anticipate and plan to accommodate.
Product and Service Cross-Selling and Up-Selling
Business managers strive to leverage customer satisfaction to cross-sell and upsell products and services, thereby increasing revenue and brand loyalty.
Maintenance Management
A business must focus on maintenance to keep equipment up and running and reduce downtime as well as perform anticipating required resources, hours on the job and the types of training required.
Customer Targeting
If a business can identify the things that cause a particular customer to buy a particular product or service, it can create products, marketing messages, advertising and outreach that will target specific customer buying behaviors and needs.
Human Resource Attrition
To retain employees, the organization must understand what makes a team member leave a position, what makes them want to stay and invest in the future of the business and what types of issues will create dissatisfaction.
Loan Approval
The cost of dealing with ‘bad’ loans is high and it reduces profitability and productivity. To succeed, businesses must have a dependable process for attracting the right clientele and reviewing, approving and managing loans.
Marketing Optimization
Businesses create targets and goals but, without a fundamental understanding of what affects sales and what kind of decision process customers use to choose a product or service, the marketing and advertising process is based only on guesswork.
Predictive Analytics Using External Data
The ability to integrate data from sources outside the enterprise is crucial to many businesses. Analysis of external data is tedious and time consuming if it is not easily handled by an augmented analytics solution.
Online Target Marketing
In order to optimize available marketing funds and resources, the enterprise must understand what works and what does not work, where to put its messaging and the ideal profile and demographic for its targeted customers.
Students’ Academic Performance
Predictive analytics of students’ academic performance can help decision makers take appropriate actions at the right moment and plan appropriate training in order to improve the student’s success rate.
Crime Type Prediction
Predict the Crime Type in order to prevent crime in the society and assist law agencies to design optimal strategies to ward off crime happenings to increase public safety and decrease economic loss.
While every business can and should develop a set of business use cases that will apply to its own unique industry, function and/or issues, your enterprise can use these sample use cases to illustrate the usefulness of augmented analytics and provoke discussion and thought on the use of analytics among the business user community.
‘Business Use Cases can be helpful in this effort, as the provide a clear picture of a story of a problem that is familiar to business users and a clear picture of how the augmented analytics solution can help the user.’
Find out how Augmented Analytics can help your business plan for success and explore the profound impact of these tools with sample Use Cases.











